QUESTION 4 OF 10
A 30-year-old female physiotherapist presents with left wrist pain and swelling with no history of trauma. X-ray demonstrates an eccentric, lytic lesion in the distal radius. MRI demonstrates a breach in the cortex with a small soft tissue component. Biopsy reveals a tumour comprising multinucleated giant cells and stromal cells. female physiotherapist presents with right wrist pain and swelling with no history of trauma. X-ray demonstrates an eccentric, lytic lesion in the distal radius. MRI demonstrates a breach in the cortex with a small soft tissue component. Biopsy reveals a tumour comprising multinucleated giant cells and stromal cells.
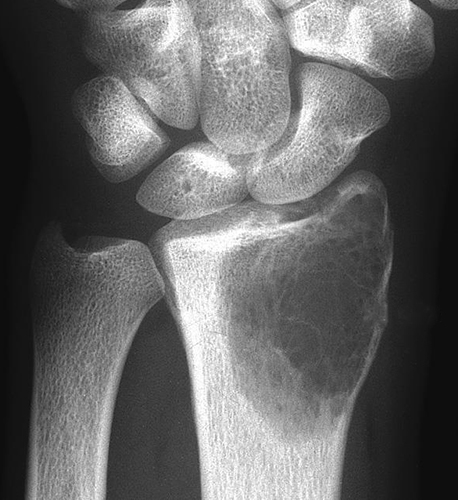
Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE about this tumour?
QUESTION ID: 1281