- When a neonate presents in the clinic with CTEV a complete head to toe examination is essential to rule out other congenital abnormalities.
- The spine and the joints should be specifically examined to rule out spina bifida and arthrogryposis.
- Differential diagnoses include metatarsus adductus ( MA) and positional clubfoot ( a foot that is fully correctable on gentle handling).
- Apart from the foot the calf muscle usually has reduced girth and length and the foot may be smaller than the contralateral side.
- Hindfoot is the key for examination and is normal in both MA and positional clubfoot but fixed and abnormal in CTEV ( and CVT). However, both MA and positional clubfoot may be associated with intra-uterine moulding and are known risk factors for DDH.
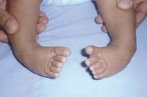
Bilateral CTEV.
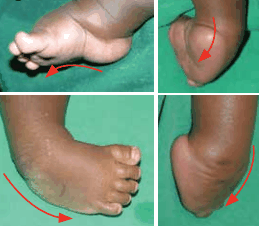
Typical deformities of CTEV. Clockwise from left: cavus, adductus, equinus, varus. From Staheli L. Clubfoot: Ponseti management. © Global help.
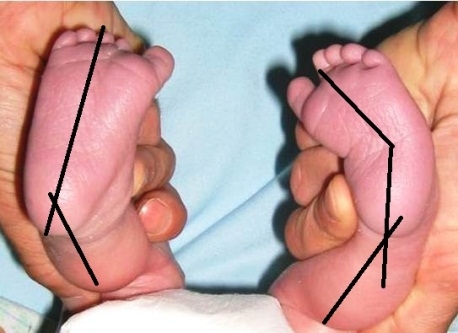
Unilateral CTEV, compared to the normal side the forefoot is adducted and the hindfoot is in varus.
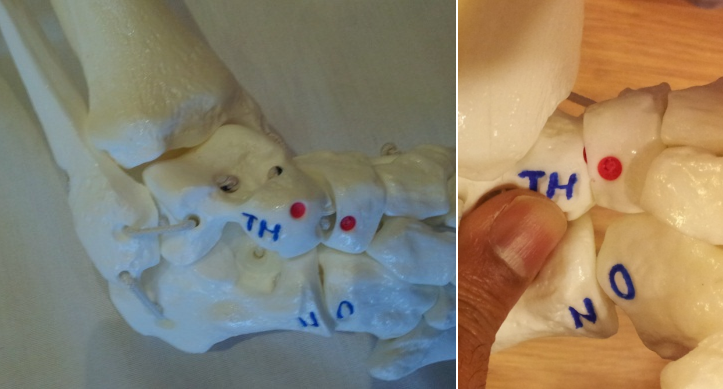
Model showing an uncorrected CTEV (left); talar head is prominent and palpable in front of lateral malleolus. Anterior calcaneal process is not palpable. Corrected CTEV (right); anterior process of calcaneum is now palpable as STJ is reduced.
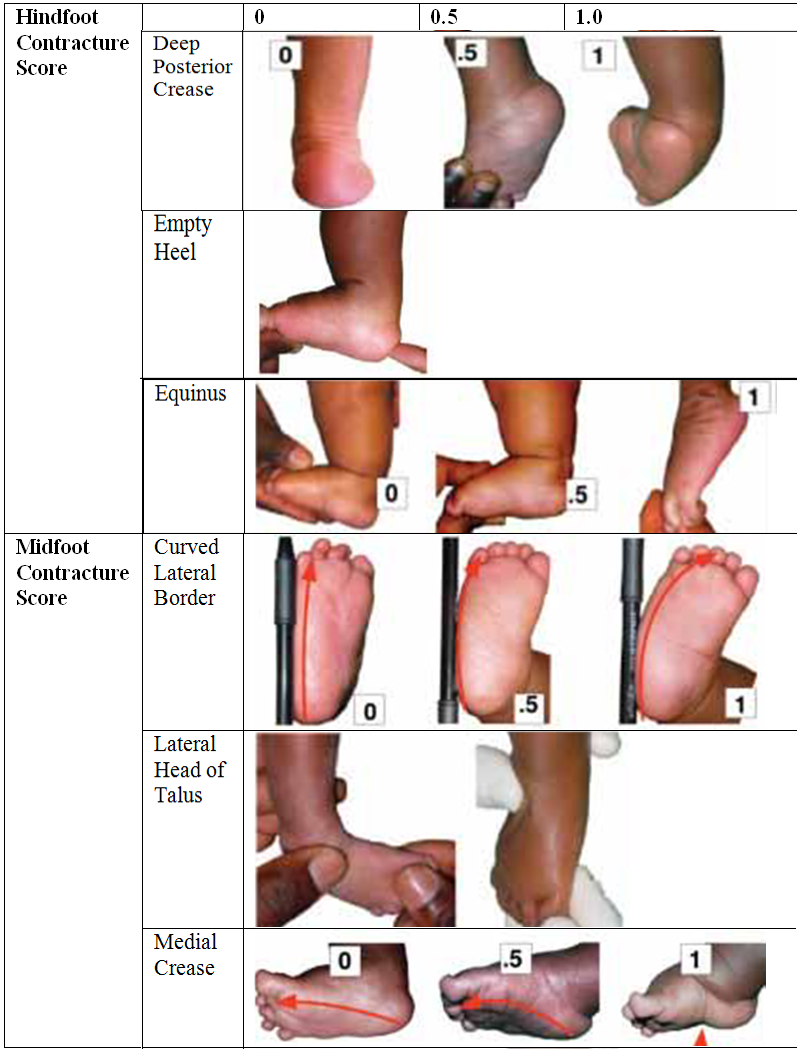
Pirani scoring:
- This is a clinical grading system of the severity of deformity.
- It does not take into account the functional state, radiological status or the gait.
- The score has been widely validated.
- It can be used to monitor the progress of treatment and is also predictive of the number of casts required.
- The assessment is divided into midfoot (3parts) and hindfoot (3 parts). Each parameter can have a score of 0, 0.5 or 1. The more severe the foot the higher the score.
- The foot and ankle should be placed in maximal correction for assessment. A sequence of look, feel, move helps to commit the steps to memory:
Hindfoot score: 0-3
Look: posterior heel crease:
Multiple fine creases: 0
One or two deep creases: 0.5
Deep creases change the contour of the arch : 1
Feel: empty heel sign:
Calcaneal tuberosity easily palpable : 0
Calcaneal tuberosity difficult to palpate : 0.5
Calcneal tuberosity not palpable: 1
Move: equinus:
Full ankle dorsiflexion : 0
Ankle in plantigrade: 0.5
Ankle in equinus: 1
Midfoot score: 0-3
Look: curvature of lateral border: ( place a pencil against the lateral border)
Straight border: 0
Mild, distal curved border: 0.5
Lateral border curves at CCJ: 1
Feel: talar head:
Talo-navicular completely reduced, talar head not felt : 0
Talo-navicular joint partially reduced, talar head difficult to feel: 0.5
Talo-navicular joint unreduced, talar head easily felt: 1
Move: medial crease: (assessed after moving the foot to corrected position)
Multiple fine creases: 0
One or two deep creases: 0.5
Deep creases change the contour of the arch: 1
- DiMeglio has proposed a 20 point classification system. Both of the scoring systems have good inter-rater reliability but none predict long term outcome.
- Most of the delegates attending a recent European consensus meeting on Clubfoot felt that the Pirani scoring method was simpler to use and favoured it over the DiMeglio scoring method.
Pirani scoring