- Treatment for a flexible flatfoot deformity is not required and the parents should be reassured.
- Orthotic and operative treatment is controversial.
- Orthoses (medial arch supports) have been shown not to promote the development of the longitudinal arch and should not be routinely prescribed (1).
- They may however relieve pain if present.
- Calf stretching exercises may be helpful if the Achilles tendon/gastrocnemius is tight.
Surgery
- Surgery is reserved for the older child with intractable symptoms unresponsive to nonsurgical options.
- A joint sparing operation-osteotomy such as a lateral column lengthening procedure with or without release of the gastrocnemius/Achilles tendon is the procedure of choice.
- Triple C osteotomies ( Medial calcaneal slide, Cuboid opening wedge and medial Cuneiform dorsal opening wedge.
- Arthroeresis of the subtalar joint (using an implant) is an option but is not without complication and the parents should be consented appropriately.
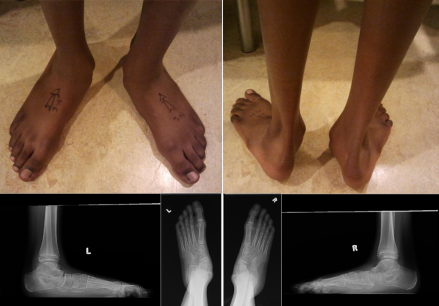
Clinical photograph and plain x-ray of a teenager with severe flat feet undergoing triple C osteotomy.
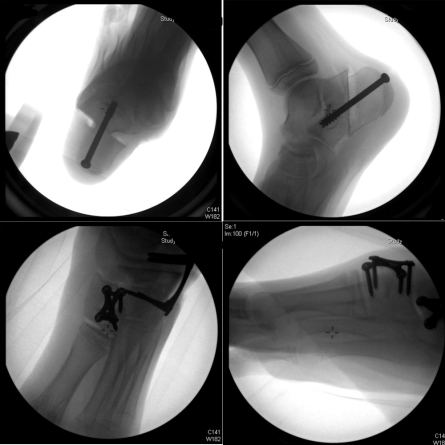
Fluoroscopy pictures of triple C osteotomies. Notice the medial calcaneal slide, Cuboid opening wedge and medical cuneiform dorsal opening wedge.
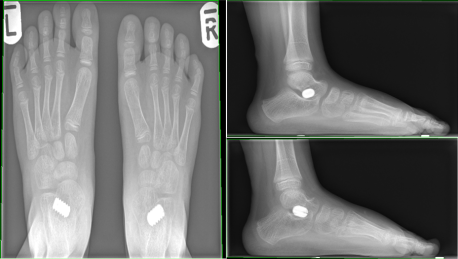
Arthrodesis for bilateral flat feet.