QUESTION 2 OF 7
27.A 70-year-old lady presents with worsening pain related to valgus knee arthritis. A plain radiograph of both knees on standing is as below(Figure 1). She is keen to consider a total knee replacement as the pain is not well controlled with analgesics and is interfering with her walking.
Which of the following is not reliable in setting external rotation of femoral component?
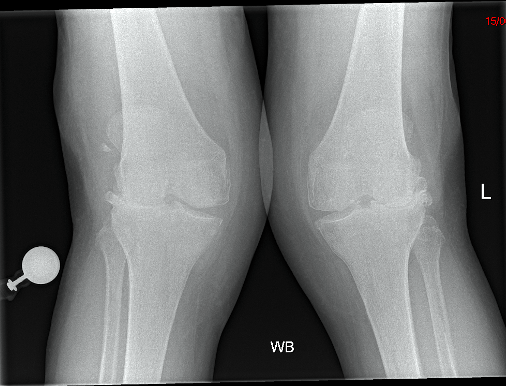
Figure 1.Anteroposterior(AP) radiographs both knees
QUESTION ID: 1192