QUESTION 4 OF 8
98.A 62-year-old male presents with pain in in his left ankle. He is a builder and owns his own business. He says he had an ankle injury many years ago. The xray is as shown. He wants to improve his pain but still wants to work. He has exhausted conservative management and whats surgery.
What surgery would be most appropriate?
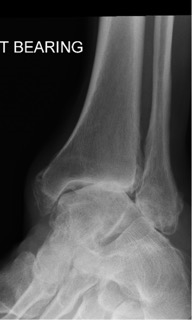
Figure 1 Anteroposterior(AP) radiograph ankle
QUESTION ID: 3296