CBD Muscle physiology
Question:“Here is a piece of paper can you draw me a sarcomere (muscle cell)?”
- Sarcomere is the basic unit of muscle.
- Contains actin (thin) and myosin (thick filaments).
- Appropriately labels parts of the diagram, including: A (anisotropic) and I (isotropic) bands, etc.
- Actin is bound to the Z line (German for “band in between”).
Question:“Tell me about the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction”
- Motor neurone discharges at neuromuscular junction.
- This causes depolarization, and action potential travels along the T tubules.
- At rest tropomyosin covers actin binding sites on the myosin protein filament, preventing cross-bridging.
- Cleavage of ATP causes a conformational change in myosin head, allowing cross-bridging between actin and myosin.
- Myosin head flexes, pulls the actin along.
- Further ATP detaches the head and cycle repeated.
- Cross-bridging allows actin filament to slide relative to myosin, which shortens sarcomere.
Question:“A lot of ATP is required for muscle contraction. Where does the energy come from? For instance, what happens in the first 60 secs when I go for a run?”
- ATP is needed for muscle contraction
- Three energy systems generate ATP
- ATP-CP system
- Anaerobic/Lactic acid system
- Aerobic system
- ATP-CP system provides an immediate pool of ATP available for a small number of muscle contractions.
- Thereafter glycolytic pathway.
- Finally an aerobic system via Krebs cycle.
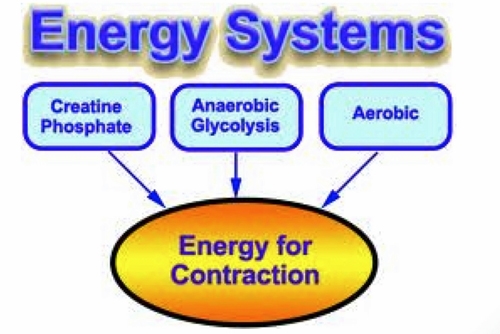
Figure 4. Energy systems