- HSMN 1, 2 and 3 are the most common.
- Diagnosis:
- EMG neuropathic
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS) slow rate of impulse conduction
- Muscle biopsy shows neuropathic pattern (uniformly small diameter fibres)
- Nerve biopsy shows demyelination
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (HSMN 1 and 2) (Figure 2)
- Autosomal dominant.
- Motor and sensory demyelinating neuropathy (motor more than sensory defects).
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) hypertrophic form (HMSN 1) – onset second decade of life.
- CMT axonal form (HSMN 2) – onset third or fourth decade, more extensive foot involvement “stork-leg”appearance.
- Orthopaedic manifestations:
- Pes cavus
- Hammer toes
- Peroneal weakness
- Stork legs/upside down champagne bottle legs
- Intrinsic muscle wasting in the hands
- Investigations –Low nerve conduction velocities in peroneal, ulnar and median nerves.
- Treatment:
- Surgery for pes cavus
- Intrinsic minus procedure for hands
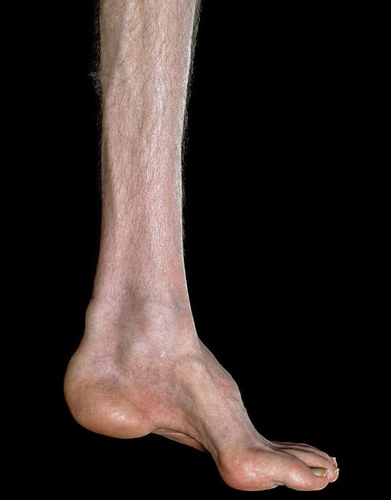
Fig 2. Charcot Marie Tooth Disease.Signs and symptoms include: weakness in the legs, ankles and feet, frequent falling, numbness and pain in legs, loss of muscle bulk in the legs and feet, hammertoes, high foot arches, decreased ability to walk and run, and footdrop.
Dejerine Sottas disease (HSMN 3)
- Autosomal recessive.
- Hypertrophic neuropathy of infancy CMT3.
Clinically:
- Delayed ambulation
- Pes cavus
- Stocking glove dysaesthesia
- Foot drop
- Spinal deformities
- Confined to wheelchair by third/fourth decade.
Riley Day syndrome
- Autosomal recessive.
- Sensory and autonomic neuropathies.
- Only in Ashkenazi Jews.
Clinically:
- Dysphagia
- Alacrima
- Pneumonia
- Excess sweating
- Postural hypotension
- Sensory loss
Hereditary sensory neuropathy
- Congenital insensitivity to pain and temperature.
- Autosomal dominant or recessive.
- Clinically Charcot joints and foot ulceration.
Friedrich’s ataxia
- Spinocerebellar disorder but may have degeneration of posterior root ganglia and peripheral nerves.
- Autosomal recessive.
- Clinical onset before the age of 10 years.
- Staggering broad-based gait, nystagmus, ataxia, cardiomyopathy, cavus foot, scoliosis, motor and sensory deficits.
- Death by 40–50 years.