Neurological assessment lower limbs
Lying
Lower Limbs
Tone, sensation, power, reflexes and peripheral pulses should be checked.
Tone
Roll leg on examination couch – assesses tone and hip pain.
If tone normal foot moves out of sequence with leg/knee. If tone normal foot moves with leg.
Sensation
Assess light touch and sharp sensation routinely. Temperature, vibration sense and two-point discrimination are useful for detailed examination.
Dermatomes
- L1 (groin)
- L2 (anterior thigh)
- L3 (anterior knee)
- L4 (anteromedial lower leg)
- L5 (lateral calf)
- S1 (sole of foot)

Figure 18.Leg dermatomes.L2 tested over anterior thigh, L3 over knee and L4 over medial lower leg.Note: Different texts use differing dermatomal maps – may be some disagreement.
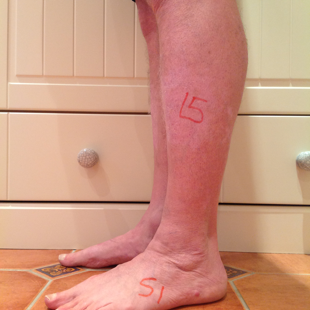
Figure 19.Foot dermatomes.L5 tested over lateral calf and dorsum of foot.S1 tested over lateral border of foot/sole of foot.
Power
Graded 0-5 using MRC scale.
Myotomes
- L2 (hip flexion)
- L3 (knee extension)
- L4 (foot dorsiflexion)
- L5 (great toe dorsiflexion)
- S1 (foot plantarflexion)
Note: Although there is far less variation in description of lower limb myotomes than upper limb it may still be helpful to describe as ‘hip flexion was 5/5’ or ‘knee extension was 4/5’.
Reflexes
- Present, Reduced, Brisk, Absent
- Quadriceps (L3/4) (to relax the quads for optimal testing ask the patient to sit on couch with legs hanging free)
- Ankle (S1)
- Plantars – rub lateral sole of foot travelling distally and across metatarsal heads
- Downgoing/Equivocal plantar reflex is a normal response
Upgoing plantar reflex suggests upper motor neurone pathology – either spinal cord or brain
Note: If up-going plantars and not previously identified then consider brain/spinal cord MRI.
If reflexes brisk then examine for clonus - >3 beats is abnormal.
(If reflexes normal do not assess for clonus)
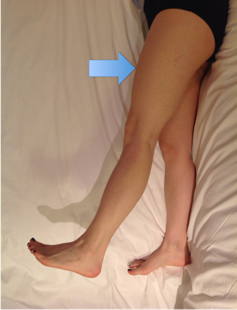
Figure 20.L2 myotome.To test against resistance apply downward pressure over mid femur (reduces mechanical advantage of tester).If power unable to resist gravity ask patient to lie on side and repeat
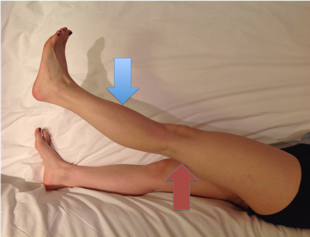
Figure 21.L3 myotome.Support leg just above knee (red arrow) and then test knee extension with downward pressure on lower leg (blue arrow)
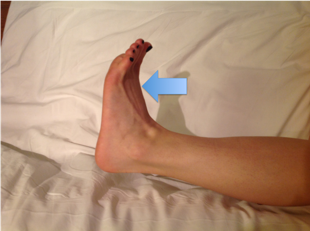
Figure 22.L4 myotome.Ask patient to dorsiflex ankle and apply resistance over forefoot as shown by blue arrow.
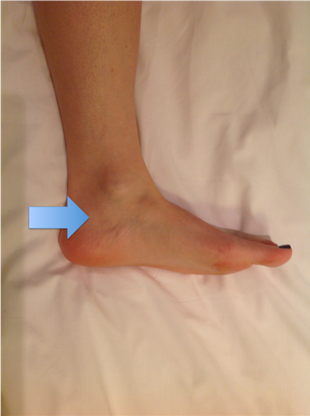
Figure 23. L5 myotome.Ask patient to extend great toe and apply resistance over great toe as shown by blue arrow.
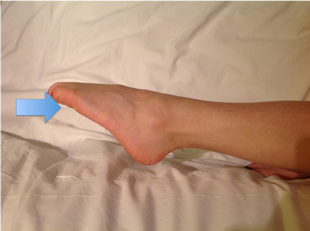
Figure 24. S1 myotome.Ask patient to plantarflex foot and apply resistance under MT heads as shown by blue arrow.