Inspection
General
Patients should be undressed from waist down
Any walking aids, splints, orthotics?
Look at hands (? Rheumatoid)
Standing
Remember to inspect from all sides (front, laterally, and from behind):
Skin
- surgical or traumatic scars,
- erythema
- bruising
- sinuses
- ulcers
Deformity
- Varus (fig1)/ valgus
- Fixed flexion (fig 2)
- Hyperextension (recurvatum)
- Limb length discrepancy - characterized by a pelvic tilt
Swelling
- Effusion/Bakers cyst
- Soft tissue
Muscle wasting (quadriceps)
Coronal plane alignment (fig 3)
- Patella position
- Q angle : angle subtended from a line drawn from ASIS to midpoint of patella and line drawn from midpoint of patella to tibial tubercle, average 15°, greater in females). (fig 4)
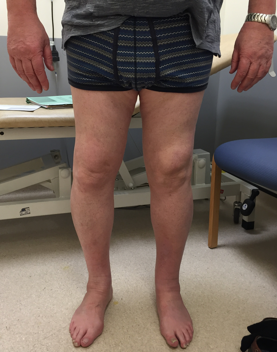
Figure 1.Clinical photograph demonstrating right knee varus deformity. Left knee demonstrates a midline surgical scar consistent with previous total knee arthroplasty.
Figure 2 .Clinical photograph demonstrating flexion deformity of right knee.
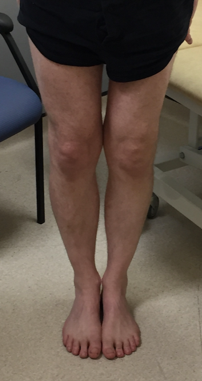
Figure 3.Coronal plane alignment assessment with the patient’s feet pointing forwards and together.
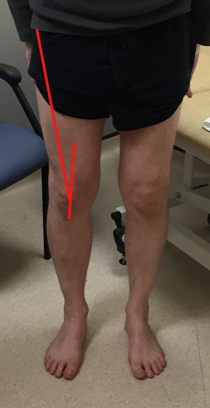
Figure 4.Q angle assessment denoted by red lines.
Patient walking
Observe the gait pattern
- Foot progression angle (10-15° external)
- Stiff knee
- Antalgic
Varus or valgus thrust
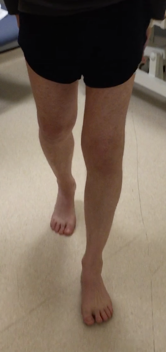
Figure 5.Clinical photograph demonstrating normal foot progression.
Patient sitting down
Legs hanging over side of couch and ask patient to extend and flex knees
- Look for J-sign (patella moves centrally then subluxes laterally as the knee comes into extension)
Figure 6 and 7.Clinical photograph demonstrating patella tracking.
Patient lying supine
Ensure patient is relaxed and monitor for discomfort when palpating.
- Effusion
- Swipe/bulge test (small)
- Patellar tap test (moderate)
- Ballotment test (massive)
Synovial hypertrophy (no effusion)
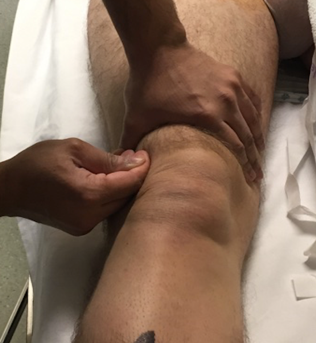
Figure 8.Clinical photograph demonstrating swipe test.
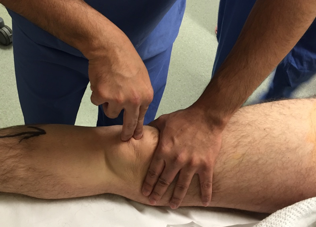
Figure 9.Clinical photograph demonstrating patellar tap test
Muscle wasting(measuring the circumference of the thigh from a fixed point such as the anterior superior iliac spine) (fig 10)
- Straight leg raise- (‘keeping your knee straight can you lift the heel off the bed’) (fig 11)
- Tests extensor mechanism
- ? hyperextension
- Assess flexion deformity, ? passively correctable
- Flex knee assessing range of flexion (‘bend your knee’)
- Palpation (fig 12)with knee at 90° and foot plantigrade on couch.
- Medial/lateral joint line
- MCL/LCL attachments on femoral and tibial condyles
- Patellar tendon
Popliteal fossa
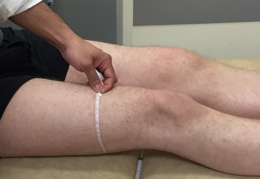
Figure 10.Clinical photograph measuring thigh circumference
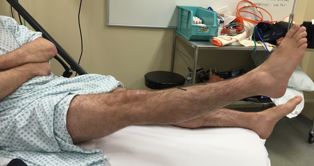
Figure 11.Clinical photograph demonstrating straight leg raise
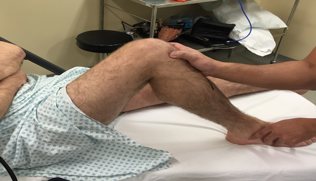
Figure 12.Clinical photograph demonstrating palpation of lateral joint line with 1 finger.